ONTAP cyber vault overview
What is a cyber vault?
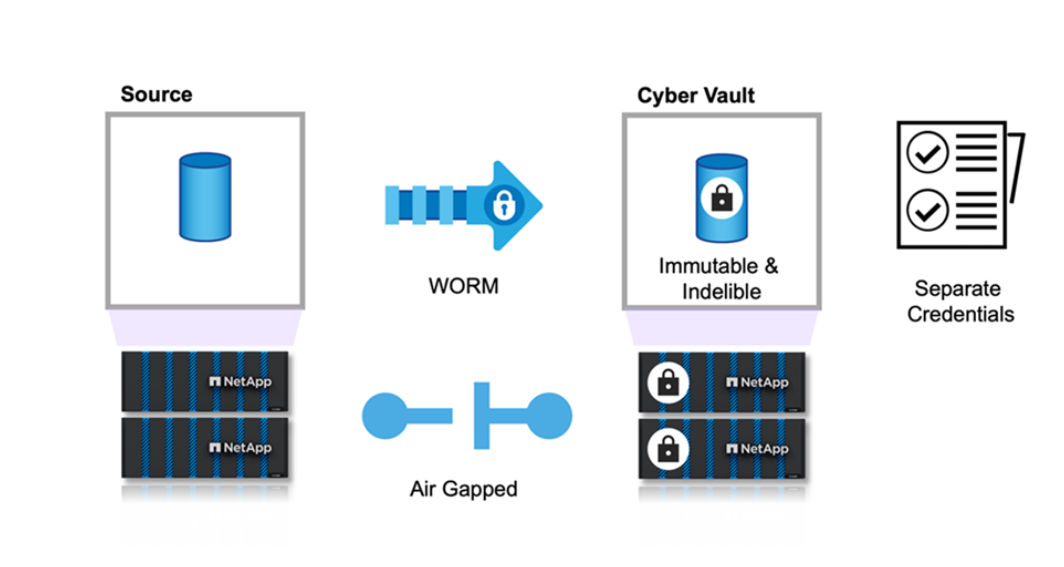
A cyber vault is a specific data protection technique that involves storing critical data in an isolated environment, separate from the primary IT infrastructure.
"Air-gapped", immutable and indelible data repository that is immune to threats affecting the main network, such as malware, ransomware, or even insider threats. A cyber vault can be achieved with immutable and indelible snapshots.
Air-gapping backups that use traditional methods involve creating space and physically separating the primary and secondary media. By moving the media offsite and/or severing connectivity, bad actors have no access to the data. This protects the data but can lead to slower recovery times.
NetApp's approach to cyber vault
Key features of NetApp reference architecture for a cyber vault include:
-
Secure, isolated storage infrastructure (e.g., air-gapped storage systems)
-
Copies of the data must be both immutable and indelible without exception
-
Strict access controls and multi-factor authentication
-
Rapid data restoration capabilities
You can use NetApp storage with ONTAP as an air-gapped cyber vault by leveraging SnapLock Compliance to WORM-protect Snapshot copies. You can perform all the basic SnapLock Compliance tasks on the Cyber vault. Once configured, Cyber vault volumes are automatically protected, eliminating the need to manually commit the Snapshot copies to WORM. More information on logical air-gapping can be found in this blog
These are the terms commonly used in cyber vault architectures.
Autonomous Ransomware Protection (ARP) - Autonomous Ransomware Protection (ARP) feature uses workload analysis in NAS (NFS and SMB) environments to proactively, and in real time, detect and warn about abnormal activity that might indicate a ransomware attack. When an attack is suspected, ARP also creates new Snapshot copies, in addition to existing protection from scheduled Snapshot copies. For more information, see the ONTAP documentation on Autonomous Ransomware Protection
Air-gap (Logical) - You can configure NetApp storage with ONTAP as a logical air-gapped cyber vault by leveraging SnapLock Compliance to WORM-protect Snapshot copies
Air-gap (Physical) - A physical air-gapped system has no network connectivity to it. Using tape backups, you can move the images to another location. The SnapLock Compliance logical air-gap is just as robust as a physical air-gapped system.
Bastion host - A dedicated computer on an isolated network, configured to withstand attacks.
Immutable Snapshot copies - Snapshot copies that are not able to be modified, without exception (including a support organization or the ability to low level format the storage system).
Indelible Snapshot copies - Snapshot copies that are not able to be deleted, without exception (including a support organization or the ability to low level format the storage system).
Tamperproof Snapshot copies - Tamperproof Snapshot copies use the SnapLock Compliance clock feature to lock Snapshot copies for a specified period. These locked snapshots can not be deleted by any user or NetApp support. You can use locked Snapshot copies to recover data if a volume is compromised by a ransomware attack, malware, hacker, rogue administrator or accidental deletion. For more information, see the ONTAP documentation on Tamperproof Snapshot copies
SnapLock - SnapLock is a high-performance compliance solution for organizations that use WORM storage to retain files in unmodified form for regulatory and governance purposes. For more information, see the ONTAP documentation on SnapLock.
SnapMirror - SnapMirror is disaster recovery replication technology, designed to efficiently replicate data. SnapMirror can create a mirror (or exact copy of the data), vault (a copy of the data with longer Snapshot copy retention), or both to a secondary system, on premises or in the cloud. These copies can be used for many different purposes such as a disaster, bursting to the cloud, or a cyber vault (when using the vault policy and locking the vault). For more information, see the ONTAP documentation on SnapMirror
SnapVault - In ONTAP 9.3 SnapVault was deprecated in favor of configuring SnapMirror using the vault or mirror-vault policy. This is term, while still used, has been depreciated as well.
Performance sizing considerations
-
What are the source platform models (FAS v AFF A-Series v AFF C-Series)?
-
What is the bandwidth and latency between the source and cyber vault?
-
How large are the file sizes and how many files?
-
What is your recovery time objective?
-
How much data do you need to be recovered within the RTO?
-
How many SnapMirror fan-in relationships will the cyber vault be ingesting?
-
Will there be single or multiple recoveries happening at the same time?
-
Will those multiple recoveries be happening to the same primary?
-
Will SnapMirror be replicating to the vault during a recovery from a vault?
Sizing examples
Here are examples of different cyber vault configurations.

For example:Calculating the needed Capacity
-
Primary dataset size = 5TB
-
Daily change rate = 5% (0.05)
-
Deduplication and compression efficiency = 50% (0.50)
Now, let us walk through the calculation:
-
Calculate the daily data change rate:
Changed data per day = 5000 * 5% = 250GB -
Calculate the total changed data for 30 days:
Total changed data in 30 days = 250 GB * 30 = 7.5TB -
Calculate the total storage required:
TOTAL = 5TB + 7.5TB = 12.5TB -
Apply deduplication and compression savings:
EFFECTIVE = 12.5TB * 50% = 6.25TB
Steps walk through
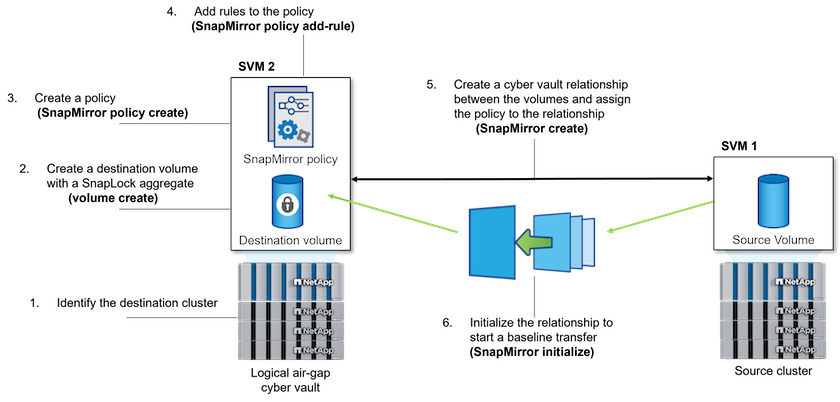
The following illustration shows the procedure for initializing a SnapLock Compliance vault relationship:
-
Identify the destination array to become the cyber vault to receive the air-gapped data.
-
On the destination array, to prepare the cyber vault, install the ONTAP One license, initialize the Compliance Clock, and, if you are using an ONTAP release earlier than 9.10.1, create a SnapLock Compliance aggregate.
-
On the destination array, create a SnapLock Compliance destination volume of type DP:
volume create -vserver SVM_name -volume volume_name -aggregate aggregate_name -snaplock-type compliance|enterprise -type DP -size size -
Beginning with ONTAP 9.10.1, SnapLock and non-SnapLock volumes can exist on the same aggregate; therefore, you are no longer required to create a separate SnapLock aggregate if you are using ONTAP 9.10.1. You use the volume
-snaplock-typeoption to specify a Compliance type. In ONTAP releases earlier than ONTAP 9.10.1, the SnapLock mode, Compliance is inherited from the aggregate. Version-flexible destination volumes are not supported. The language setting of the destination volume must match the language setting of the source volume.The following command creates a 2 GB SnapLock Compliance volume named
dstvolBinSVM2on the aggregatenode01_aggr:cluster2::> volume create -vserver SVM2 -volume dstvolB -aggregate node01_aggr -snaplock-type compliance -type DP -size 2GB -
On the destination cluster, to create the air-gap, set the default retention period, as described in Set the default retention period.
A SnapLock volume that is a vault destination has a default retention period assigned to it. The value for this period is initially set to a minimum of 0 years and maximum of 100 years (Beginning with ONTAP 9.10.1. For earlier ONTAP releases, the value is 0 - 70.) for SnapLock Compliance volumes. Each NetApp Snapshot copy is committed with this default retention period at first. The default-retention-period must be changed. The retention period can be extended later, if needed, but never shortened. For more information, see Set retention time overview.Service providers should consider customer's contract end dates when determining retention period. For example, if the cyber vault retention period is 30 days and the customer's contract ends before the retention period expires, data in the cyber vault can not be deleted until the retention period expires. -
Create a new replication relationship between the non-SnapLock source and the new SnapLock destination you created in Step 3.
This example creates a new SnapMirror relationship with destination SnapLock volume dstvolB using a policy of XDPDefault to vault Snapshot copies labeled daily and weekly on an hourly schedule:
cluster2::> snapmirror create -source-path SVM1:srcvolA -destination-path SVM2:dstvolB -vserver SVM2 -policy XDPDefault -schedule hourlyCreate a custom replication policy or a custom schedule if the available defaults are not suitable.
-
On the destination SVM, initialize the SnapVault relationship created in Step 5:
snapmirror initialize -destination-path destination_path -
The following command initializes the relationship between the source volume srcvolA on SVM1 and the destination volume dstvolB on SVM2:
cluster2::> snapmirror initialize -destination-path SVM2:dstvolB -
After the relationship is initialized and idle, use the snapshot show command on the destination to verify the SnapLock expiry time applied to the replicated Snapshot copies.
This example lists the Snapshot copies on volume dstvolB that have the SnapMirror label and the SnapLock expiration date:
cluster2::> snapshot show -vserver SVM2 -volume dstvolB -fields snapmirror-label, snaplock-expiry-time
Cyber vault hardening recommendations
-
Isolate the cyber vault's management planes
-
Do not enable data LIFs on the destination cluster as they are an additional attack vector
-
On the destination cluster, limit intercluster LIF access to the source cluster with a service policy
-
Segment the management LIF on the destination cluster for limited access with a service policy and a bastion host
-
Restrict all data traffic from the source cluster to the cyber vault to allow only the ports required for SnapMirror traffic
-
Where possible, disable any unneeded management access methods within ONTAP to decrease the attack surface
-
Enable audit logging and remote log storage
-
Enable multi-admin verification and require verification from an admin outside your regular storage administrators (e.g. CISO staff)
-
Implement role-based access controls
-
Require administrative multifactor authentication for System Manager and ssh
-
Use token based authentication for scripts and REST API calls
ONTAP software recommendations
Beginning with ONTAP 9.14.1, you can specify retention periods for specific SnapMirror labels in the SnapMirror policy of the SnapMirror relationship so that the replicated Snapshot copies from the source to the destination volume are retained for the retention-period specified in the rule. If no retention period is specified, the default-retention-period of the destination volume is used.
Beginning with ONTAP 9.13.1, you can instantaneously restore a locked Snapshot copy on the destination SnapLock volume of a SnapLock vault relationship by creating a FlexClone with the snaplock-type option set to "non-snaplock" and specifying the Snapshot copy as the "parent-snapshot" when executing the volume clone creation operation. Learn more about creating a FlexClone volume with a SnapLock type.
Is cyber vault a product from NetApp?
No, "cyber vault" is an industry wide term. NetApp has created a reference architecture to make it easy for customers to build their own cyber vaults and leverage the dozens of ONTAP security features to help protect their data from cyber threats. More information is available on the ONTAP documentation site.
To learn more about the information described in this cyber vault information, refer to the following additional information and security concepts.


No Comments